Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is a possibly dangerous disease brought about by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi. Albeit generally preventable and treatable, it stays a critical wellbeing concern, particularly in emerging nations where sterilization and admittance to clean water are restricted. The World Wellbeing Association (WHO) gauges that 11 to 21 million individuals universally contract typhoid every year, prompting roughly 128,000 to 161,000 passings. Tending to the test of typhoid fever requires figuring out its causes, transmission, side effects, and long haul arrangements that attention on avoidance, better wellbeing framework, and admittance to viable clinical consideration.
The Issue: Grasping Typhoid Fever
Causes and Transmission
Typhoid fever is brought about by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi, which spreads through ingestion of food or water polluted with dung from a tainted individual. The most widely recognized methods of transmission include:
Defiled Water: In locales without legitimate sewage frameworks or water treatment offices, Salmonella Typhi can undoubtedly pollute water sources.
Poor Sanitation: Insufficient garbage removal practices and open poo are basic factors that add to the spread of the microscopic organisms.
Perilous Food Handling: Food arranged in unhygienic circumstances, especially in road food markets or in families without admittance to clean water, can convey the microorganisms.
In many emerging countries, these variables join to establish a climate where typhoid fever can flourish. The absence of framework for clean water and appropriate sterilization in thickly populated regions makes the spread of the sickness challenging to contain.
Side effects and Effect
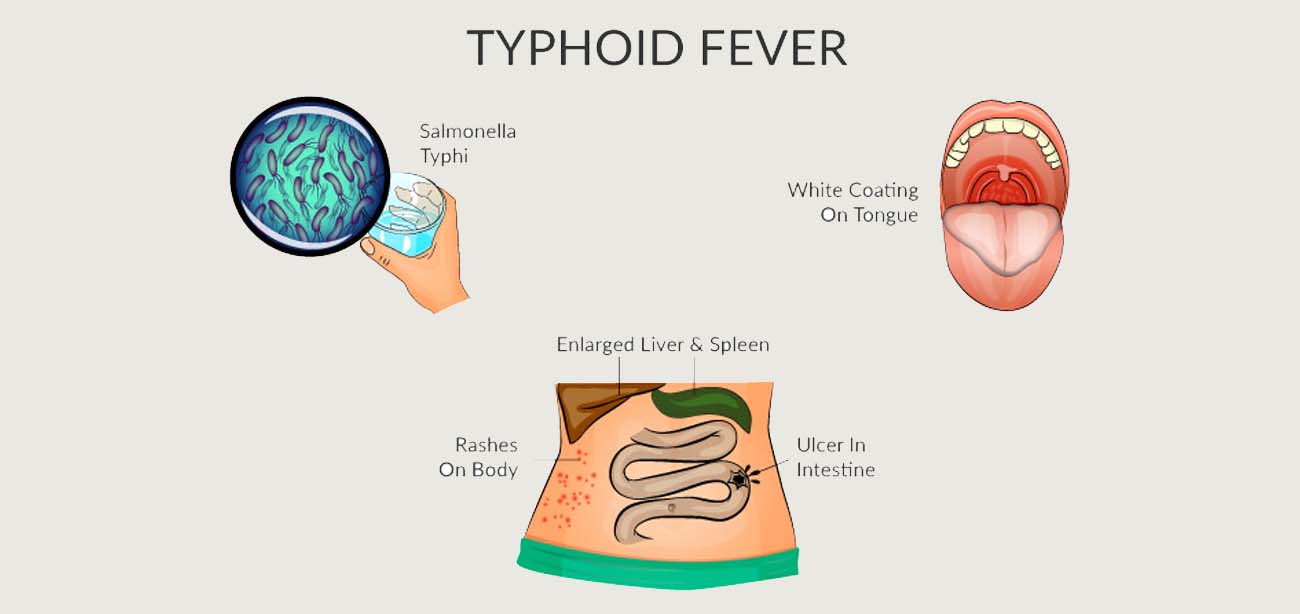
When inside the body, Salmonella Typhi attacks the digestion tracts and circulation system, prompting a scope of side effects. The beginning is normally continuous, starting 6 to 30 days after openness. Normal side effects include:
Fever: High, supported fever, which can reach up to 104°F (40°C).
Shortcoming and Fatigue: Tenacious sleepiness, which can cripple.
Stomach Pain: Stomach spasms and torment, frequently joined by looseness of the bowels or obstruction.
Headaches: Extraordinary cerebral pains are normal during contamination.
Rash: at times, a rash of level, rose-shaded spots can foster on the mid-region and chest.
Loss of Appetite: Prompting weight reduction in delayed cases.
Whenever left untreated, typhoid fever can prompt serious difficulties like inward dying, digestive hole, or even demise. The sickness excessively influences youngsters and those with debilitated invulnerable frameworks. In any case, with appropriate treatment, the death rate drops fundamentally.
General Wellbeing and Financial Weight
The general wellbeing and financial effects of typhoid fever are significant. In low-pay nations, typhoid fever adds to high dismalness and death rates, particularly among weak populaces. The medical services framework frequently becomes overpowered because of the sheer number of cases, which redirects assets from other basic medical problems. The expenses of treating typhoid, especially for the people who foster medication safe strains, put a critical monetary weight on the two people and legislatures.
In addition, the monetary effect goes past medical services costs. Individuals experiencing typhoid fever are frequently unfit to work, which lessens efficiency. In people group where the illness is endemic, continuous flare-ups can restrict instructive open doors as kids miss school and further debilitate neighborhood economies that depend on predictable work yield.
The Test of Medication Safe Typhoid
Perhaps of the most disturbing advancement lately is the ascent of multidrug-safe (MDR) typhoid fever. Salmonella Typhi has become impervious to normal anti-infection agents like chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, which were once the principal line of treatment. The rise of widely drug-safe (XDR) strains has muddled the treatment cycle significantly further, as these strains are impervious to a more extensive scope of anti-microbials, leaving restricted helpful choices.
MDR and XDR typhoid fever represent a grave danger to general wellbeing, especially in districts where admittance to cutting edge clinical consideration is restricted. Treating drug-safe typhoid is more costly, takes more time, and accompanies a more serious gamble of confusions and mortality. This challenge highlights the requirement for far reaching arrangements that address both the actual infection and the developing issue of anti-toxin opposition.
Answers for Typhoid Fever
Resolving the issue of typhoid fever requires a multi-pronged methodology that incorporates counteraction, further developed medical care foundation, and more successful therapies. The arrangements can be assembled into the accompanying classifications:
1. Further developed Sterilization and Admittance to Clean Water
The best long haul answer for typhoid fever is to handle its underlying drivers — unfortunate sterilization and absence of clean water. States and global associations should put resources into foundation that gives:
Safe Drinking Water: Water decontamination frameworks, appropriate filtration strategies, and dependable dispersion of clean water are essential to forestalling the spread of *Salmonella Typhi*.
Sterilization Facilities: Building appropriate sewage frameworks and giving admittance to safe latrines can radically lessen the occurrence of waste pollution in food and water sources.
Cleanliness Education: General wellbeing efforts ought to zero in on teaching networks about the significance of handwashing, safe food arrangement, and legitimate garbage removal. Conduct change at the local area level can fundamentally decrease the spread of the microbes.
Associations like UNICEF and the WHO have long upheld for "Water, Sterilization, and Cleanliness" (WASH) projects to be focused on in emerging countries. These projects center around giving the fundamental framework and advancing clean practices, particularly in rustic and metropolitan ghetto regions where typhoid fever is generally uncontrolled.
2. Immunization
Immunization is one more key part in the battle against typhoid fever. As of now, two kinds of immunizations are accessible:
Ty21a (oral vaccine): A live, lessened immunization that is regulated orally in four portions.
Vi polysaccharide immunization (injection): A solitary portion injectable immunization.
The two immunizations give assurance, yet their inclusion is restricted. A more current immunization, known as Typbar-TCV (Typhoid Form Antibody), has shown more noteworthy viability, especially in more youthful youngsters, and can be managed in a solitary portion with longer-enduring resistance.
Extending admittance to these immunizations, particularly in regions with high transmission rates, is critical. Inoculation crusades, upheld by state run administrations and worldwide wellbeing associations, are fundamental for controlling episodes and diminishing the general occurrence of the infection.
3. Improved Observation and Analysis
Early recognition of typhoid fever is basic for successful treatment and control. Numerous nations with high typhoid frequency don't have hearty reconnaissance frameworks, making it challenging to follow and answer episodes. Reinforcing reconnaissance endeavors includes:
Further developed Research center Facilities: Laying out exceptional labs for blood societies and sub-atomic testing is fundamental for precise analysis. Speedy recognizable proof of the microscopic organisms can prompt convenient treatment and forestall the spread of the infection.
Routine Information Collection: States ought to execute and keep up with data sets that track instances of typhoid fever, noticing the pervasiveness of medication safe strains, immunization inclusion, and other epidemiological information. This information can direct general wellbeing arrangements and mediation systems.
Quick Analytic Tests: Putting resources into point-of-care demonstrative devices that can be utilized in remote or asset unfortunate settings will upgrade early determination and treatment.
4. Tending to Anti-infection Opposition
The ascent of anti-infection opposition in typhoid fever requires a more careful and vital way to deal with treatment. This incorporates:
Reasonable Utilization of Antibiotics: Abuse and abuse of anti-microbials in many areas of the planet have added to the rise of medication safe strains. Wellbeing specialists should uphold stricter rules on anti-toxin remedies and advance the utilization of tight range anti-infection agents when proper.
Innovative work of New Antibiotics: Drug organizations and exploration establishments ought to be boosted to foster new anti-toxins that can successfully battle MDR and XDR typhoid. Public-private organizations can assist with financing research that spotlights on making new medicines for drug-safe strains.
Worldwide Participation on Opposition Monitoring: Global joint effort is expected to screen the spread of safe strains. This can be accomplished through an organized worldwide organization that shares information and assets for answering flare-ups of medication safe typhoid fever.
5. Wellbeing Framework Fortifying
Wellbeing frameworks in numerous endemic locales are frequently overburdened and underfunded. Reinforcing these frameworks is urgent to forestalling and overseeing typhoid fever episodes. This includes:
Preparing Medical care Workers: Medical care laborers should be prepared to perceive the side effects of typhoid fever, especially in its beginning phases, and to direct the suitable therapy. Constant schooling on anti-toxin stewardship is likewise essential to forestall the abuse of medications.
Expanding Admittance to Healthcare: Further developing medical care access in provincial and underserved regions will guarantee that individuals can get opportune analysis and therapy. Versatile centers, telemedicine, and local area wellbeing projects can overcome any barrier between medical services offices and far off populaces.




0 Comments